2020 Montana Cool-Season Spring Pulse Variety Evaluation Annual Report
Prepared By: William Franck, Sooyoung Franck and Chengci Chen
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
The Montana State University Eastern Agricultural Station in Sidney, MT coordinates an annual variety evaluation for cool season spring pulse crops (dry pea, lentil and chickpea) at multiple locations across the state of Montana. In 2020, funding for this project was obtained from the Montana Agricultural Experiment Station, the USA Dry Pea and Lentil Council, and testing fees from private entities submitting varieties and experimental lines for evaluation. The results provided in this report reflect the efforts of a large team of individuals from the Montana State University Agricultural Experiment Stations, Montana State University Extension, industrial partners from the seed industry and cooperating producers across the state. The following list provides contact information for many of the individuals involved in the 2020 variety evaluation.
Montana State University
Chengci Chen: Superintendent/Professor, Eastern Ag. Research Center
1501 North Central Ave, Sidney, MT 59270
(406) 433-2208, cchen@montana.edu
William Franck: Research Scientist, Eastern Ag. Research Center
1501 North Central Ave, Sidney, MT 59270
(406) 433-2208, william.franck@montana.edu
Kevin McPhee: Professor, Pulse Breeder, Plant Science and Plant Pathology
Bozeman, MT 59717
(406) 994-5156; kevin.mcphee@montana.edu
Frankie Crutcher, Assistant Professor, Eastern Ag Research Center
1501 North Central Avenue Sidney, MT, 59270
(406) 433-2208, frankie.crutcher@montana.edu
Sooyoung Franck: Research Associate, Eastern Ag. Research Center
1501 North Central Ave, Sidney, MT 59270
(406) 433-2208, sooyoung.franck@montana.edu
Patrick Carr: Superintendent/Associate Professor, Central Ag Research Center
52583 US Hwy 87, Moccasin, MT, 59462
(406) 423-5421, patrick.carr@montana.edu
Simon Fordyce: Research Associate
52583 US Hwy 87, Moccasin, MT, 59462
(406) 423-5421, simon.fordyce@montana.edu
Kent McVay: Associate Professor, Southern Ag Research Center
748 Railroad Hwy Huntley, MT, 59037
(406) 348-3400, kmckvay@montana.edu
Peggy Lamb: Research Scientist, Northern Ag. Research Center
3710 Assiniboine Road Havre, MT 59501
(406) 265-6115, plamb@montana.edu
Inga Hawbaker, Daniels County Extension Agent
106 Railroad Ave East Scobey, MT 59263
(406) 487-2861, inga.hawbaker@montana.edu
Shelley Mills, Valley County Extension Agent
501 Court Square Glasgow, MT 59230
(406) 228-6241, smills@montana.edu
Qasim Khan, Research Scientist, Southern Ag Research Center
748 Railroad Hwy Huntley, MT, 59037
(406) 348-3400, qkhan@montana.edu
USDA - Agricultural Research Service
George Vandemark: Research Geneticist, USDA-ARS
Pullman, WA 99164
(509) 335-7728, George.vandemark@ars.usda.gov
Rebecca McGee: Research Geneticist, USDA-ARS
Pullman, WA 99164
(509) 335-0300, Rebecca.mcgee@ars.usda.gov
North Dakota State University
Nonoy Bandillo: Assistant Professor, Pulse Breeder, Department of Plant Science
Fargo, ND
(701) 231-8056, nonoy.bandillo@ndsu.edu
Producers
Richard Fulton: Richland, MT
Marvin Tarum: Richland, MT
Keith and Karen Schott: Broadview, MT
Industries
USA Dry Pea and Lentil Council
2780 W. Pullman Road Moscow, ID 83843
(208) 882-3023
pulse@pea-lentil.com; www.pea-lentil.com
Kurt Braunwart, Nancy Powell, and Mike Wood
ProGene
860 S. Crestline Othello, WA, 99344
(509) 448-3977, kurt@progenellc.com; nancy@progenellc.com; mike@progenellc.com
Northern Pulse Growers Association
1710 Burnt Boat Drive Bismarck, ND 58503
(701) 222-0128, info@northernpulse.com; www.northernpulse.com
Samantha Kok, Mark Kok
Valesco Genetics
PO Box 128, Plaza, ND, 58771
(701) 497-3082, sam@valescogenetics.com,mark@greatnorthernag.com
Charlie Cahill
Cahill Seeds
669 Highway 5, Scobey, MT 59263
(406) 783-5510, cahillseeds@nemontel.net
Tyler Kress
Pulse USA
2002 Northern Plains Drive
Bismarck, ND 58504
(701) 530-0734, tyler@pulseusa.com
Martin Hochhalter
Meridian Seeds
216553 37th St. SE, Suite 3, Mapleton, ND
(204) 988-4681, mhochhalter@meridianseeds.com
Richard Roland/Cody Roland
Legume Logic
(701) 965-6058, legumel@nccray.com
DISCLAIMER
The information given herein is supplied with the understanding that no discrimination is intended and no endorsement by the Montana Agricultural Experiment Station is implied. The results of individual trials and studies are considered to be of a PRELIMINARY nature and should NOT be considered as a product endorsement or recommendation for commercial use.
Project Description and Objective
Project Description
Cool season spring pulse crop (dry pea, lentil and chickpea) acreage in Montana has increased more than 10 fold this century. In an effort to improve yield and quality of these crops, the Eastern Agricultural Research Center (EARC) of Montana State University (MSU) is currently coordinating a statewide pulse crop variety evaluation project across Montana on an annual basis. For the 2020 growing season, trials were conducted at four MSU Agricultural Research Centers, the MSU-Bozeman Post Farm and two cooperating producers’ fields near Broadview and Richland, Montana. The results reported herein are intended to aid producers and seed suppliers in variety selection as well as aiding the research community in variety development. The report is available both in print and electronic formats and can be found at: agresearch.montana.edu/earc/annualreports.html.
Objective
The objective of this project is to evaluate yield and seed quality parameters for dry pea, lentil and chickpea varieties and lines selected by stakeholder input across a broad range of Montana environments.
Methods
Procedures and Experimental Design
Seed companies and pulse breeders with an interest in Montana pulse production were invited to submit commercial varieties or expermential lines for evaluation in 2020. Locations available for evaluation were indicated in the invitation letter and the selection of locations for each entry to be evaluated was determined by the submitting party. In addition, eight dry pea, six lentil and eight chickpea entries were selected by the EARC to serve as check varieties and were planted at all locations. In 2020 the variety evaluations were performed at six dryland locations and two irrigated locations.
Seed for all entries were sent to the EARC where each seed lot was tested for germintation. All seeds were treated with Obvius Fungicide (BASF Corporation, Research Triangle Park, NC) and Cruiser 5FSInsecticide (Syngenta Crop Protection, Inc., Greensboro, NC) prior to packaging. Seeds were packaged on a per plot basis to obtain live seed rates of 8, 12 and 4 live seeds per ft2 for pea, lentil and chickpea, respectively. Seeds were sent to the cooperating research centers with an appropriate rhizobial inoculant to be applied at planting. Research plots were planted in a randomized complete block design with four replicates per entry. Plot size varied amongst locations and was dictated by the equipment available at each location. Management practices varied by location but were consistent with typical practices for the location. In season measurements and harvest data were collected by each cooperating center and sent to the EARC for analysis. Grain yield data was adjusted to 13% moisture content before statistical analysis. Dry pea protein concentrations were determined using an Infratec NOVA (Foss, Hilleroed, Denmark). Analysis of variance was performed in R (version 4.0.3)andLSD was derived from the agricolae package (version 1.3-3) for mean comparison whenever the F-test is significant at P<0.05.
List of Collaborators and Locations
The type of crop (pea, lentil and chickpea) and number of entries for each of these crops evaluated at the different locations varied from location to location depending on the interest of seed suppliers and availability of resources at the respective location. The list of location, collaborators and the type of crops evaluated at each location is shown in Table 1.
Table 1. Collaborators, locations and crops evaluated in 2020
| Location | Collaborator | Irrigation | Crops Evaluated | Observations | ||
| Pea | Lentil | Chickpea | ||||
| Bozeman Post Farm | PSPP | No | X | X | X | |
| Broadview | SARC | No | X | |||
| Havre | NARC | No | X | X | X | Ascochyta damage on chickpeas |
| Huntley Dryland | SARC | No | X | X | Peas and lentils lost to grasshoppers, Ascochyta damage on chickpeas | |
| Huntley Irrigated | SARC | Yes | X | X | Chickpeas lost to Ascochyta | |
| Moccasin | CARC | No | X | X | Ascochyta damage on chickpeas | |
| Richland | EARC | No | X | X | Ascochyta damage on chickpeas | |
| Sidney Irrigated | EARC | Yes | X | X | ||
†CARC = Central Agricultural Research Center, EARC = Eastern Agricultural Research Center, PSPP = Plant Sciences and Plant Pathology, NARC = Northern Agricultural Research Center, SARC = Southern Agricultural Research Center, ‘X’ indicates the collaborator participated for the specific crop variety evaluation in 2020.
List of Varieties
Table 2 includes the list of varieties and experimental lines evaluated in 2020. Additional information for these entries can be obtained by contacting the respective seed suppliers listed in the acknowledgements section. Entries listed in this table include varieties requested by seed suppliers, varieties selected as check varieties by the Montana Agricultural Experiment Station and experimental lines from the Montana State University and North Dakota State University pulse crop breeding programs.
Table 2. Dry pea, lentil and chickpea entries included in 2020 variety evaluation trials.
| Entry | Seed Color/Size | Maturity |
| Dry Pea | ||
| AAC Asher | Yellow | Early/Medium |
| AAC Carver | Yellow | Early |
| AAC Chrome | Yellow | Medium |
| AAC Comfort | Green | Medium |
| AAC Profit | Yellow | |
| AC Agassiz | Yellow | Medium |
| AC Earlystar | Yellow | |
| Aragorn | Green | Medium |
| Bluemoon | Green | Medium |
| CDC Amarillo | Yellow | Medium |
| CDC Dakota | Yellow | Medium |
| CDC Greenwater | Green | Medium |
| CDC Inca | Yellow | Medium |
| CDC Saffron | Yellow | Medium |
| CDC Spectrum | Yellow | Medium |
| CDC Striker | Green | Medium |
| Daytona | Green | Medium/Late |
| Delta | Yellow | Medium |
| DL Apollo | Yellow | Medium |
| DS-Admiral | Yellow | Medium |
| Durwood | Yellow | Medium |
| Empire | Green | Late |
| Fairway | Green | |
| Ginny 2 | Green | |
| Goldenwood | Yellow | |
| Hampton | Green | Medium |
| Hyline | Yellow | Medium |
| Jetset | Yellow | Medium |
| Korando | Yellow | Early |
| LG Amigo | Yellow | Early/Medium |
| LG Sunrise | Yellow | Medium |
| Majestic | Yellow | |
| Majoret | Green | Medium |
| MS-19YP3 | Yellow | |
| ND Dawn | Yellow | Early |
| NDP100144G | Green | |
| NDP160028 | Green | |
| Nette 2010 | Yellow | Early/Medium |
| Orchestra | Yellow | |
| Pro 093-7410 | Yellow | |
| Pro 133-6243 | Yellow | |
| Pro 141-6258 | Green | |
| Pro 143-6220 | Yellow | |
| Pro 143-6230 | Yellow | |
| Pro 153-7409 | Yellow | |
| Pro 171-7665 | ||
| PSO877MT457 | ||
| PSO877MT632 | Yellow | |
| Salamanca | Yellow | Early |
| Shamrock | Early | |
| Yellowstone | Yellow | |
Precipitation and Cultural Practices
Precipitation, site information and agronomic management practices for the respective locations are summarized in Tables 3 and 4.
Table 3. Site characteristics for each trial location
| Bozeman | Havre | Huntley | Moccasin | Richland | Sidney | |
| Soil Type | Bozeman Silt Loam | Telstad Clay Loam & Hillon Clay Loam | Lohmiller Silty Clay Loam | Danvers-Judith Clay Loam | Farnuf Loam | Savage Silty Clay Loam |
| Elevation (ft) | 4775 | 2699 | 3022 | 4250 | 2950 | 2200 |
| Seasonal Precipitation (April-August) (in) | 6.5 | 5.6 | 8.6 | 8.6 | 5.1 | |
| Average Precipitation (April-August) (in) | 8.0 | 7.9 | 10.2 | 9.6 | ||
| Irrigation (in) | 3.5 | 3.6 |
Table 4. Major agronomic management practices for each location in 2019
| Location | Tillage | Seeding Date | Harvest Date | Previous Crop | Fertilizer | Pesticide Application |
| Pea Trials | ||||||
| Bozeman | No-Till | 4/28 | 8/19 | Barley | None | Sharpen @ 1 oz/ac; Prowl @ 24 oz/ac |
| Broadview | No-Till | 4/10 | 8/13 | Spring Wheat | None | |
| Havre | No-Till | 4/22 | 7/28 | Winter Wheat | None | Quiz @ oz/ac; Basagran @ 8 oz/ac; Mustang Max @ 4 oz/ac |
| Huntley Irrigated |
No-Till | 4/21 | 8/6 | Spring Wheat | None | RT3 @ 32 fl oz/ac, Prowl @ 32 fl oz/ac & Outlook @ 16 oz/ac on 4/20 |
| Moccasin | No-Till | 4/28 | 8/5 | Barley | 20-30-20-10 @ 50 lb/ac | RT3 @ 32 fl oz/ac pre-plant; Grizzly Too @ 1.9 fl oz/ac |
| Richland | No-Till | 5/6 | 8/18 | Spring Wheat | None | RT3 @ 32 fl oz/ac, anthem flex @ 3.5 oz/ac & Intensity @ 6 oz/ac |
| Sidney | Conventional | 4/23 | 7/31 | Sugarbeet | None | Outlook @ 12 oz/ac Premergence |
| Lentil Trials | ||||||
| Bozeman | No-Till | 4/28 | 8/19 | Barley | None | Sharpen @ 1 oz/ac; Prowl @ 24 oz/ac |
| Havre | No-Till | 4/24 | 8/2 | Winter Wheat | None | Quiz @ oz/ac |
| Huntley Irrigated |
No-Till | 4/21 | 8/6 | Spring Wheat | None | RT3 @ 32 fl oz/ac, Prowl @ 32 fl oz/ac & Outlook @ 16 oz/ac on 4/20 |
| Moccasin | No-Till | 4/28 | 8/6 | Barley | 20-30-20-10 @ 50 lb/ac | RT3 @ 32 fl oz/ac pre-plant |
| Richland | No-Till | 5/6 | 8/27 | Spring Wheat | None | RT3 @ 32 fl oz/ac, anthem flex @ 3.5 oz/ac & Intensity @ 6 oz/ac |
| Sidney | Conventional | 4/23 | 8/6 | Sugarbeet | None | Outlook @ 12 oz/ac Premergence |
| Chickpea Trials | ||||||
| Bozeman | No-Till | 4/28 | 9/16 | Barley | None | Sharpen @ 1 oz/ac; Prowl @ 24 oz/ac |
| Havre | No-Till | 5/4 | 8/18 | Winter Wheat | None | Quiz @ oz/ac |
| Huntley Dryland |
No-Till | 4/20 | 8/19 | Spring Wheat | None | RT3 @ 32 fl oz/ac, Prowl @ 32 fl oz/ac & Outlook @ 16 oz/ac on 4/20 |
| Moccasin | No-Till | 5/13 | 9/3 | Barley | 20-30-20-10 @ 50 lb/ac | RT3 @ 32 fl oz/ac pre-plant; Tricor DF @ 4 oz/ac |
| Richland | No-Till | 5/6 | 9/3 | Spring Wheat | None | RT3 @ 32 fl oz/ac, anthem flex @ 3.5 oz/ac & Intensity @ 6 oz/ac |
| Sidney | Conventional | 4/23 | 8/26 | Sugarbeet | None | Outlook @ 12 oz/ac Premergence; Miravis Top @ 14 oz/ac on 6/24 and 7/15 |
Results
Dry Pea Variety Evaluation in 2020
Fifty one dry pea varieties and experimental lines (34 yellow and 17 green) were evaluated in 2020 at seven locations, two of which were irrigated. One additional dryland location at Huntley was lost to grasshoppers prior to harvest. Eleven entries of pea (four yellow and seven green) including advanced breeding lines and check varieties selected by the EARC were tested at all locations. The remaining 40 entries were tested only at locations requested by the seed supplier. The data collected and presented includes grain yield, seed protein, thousand kernel weight, test weight, plant height and number of days to flowering consistent with previous years. As in the past, results are presented in two groups based on cotyledon color (yellow and green).
Yellow dry pea grain yield
Yellow dry pea mean grain yield for the different locations ranged from 2717 lb/ac at Broadview to 4685 lb/ac under irrigation at Huntley (Table 5). The Richland and Havre locations had excellent yields. Yields at the remaining locations were average to slightly above average. Significant yield differences were observed amongst the entries at all locations except Bozeman and Huntley (Irrigated).
Yellow dry pea protein content
Protein content is presented in Table 6. The mean protein content by location varied from 21.5% at Sidney under irrigation to 26.1% at Bozeman. Average protein content at Bozeman was 4.5% higher in 2020 compared to 2019. Historically, Mocassin and Richland have been the locations best suited protein production in dry peas and this trend held in 2020 (with the exception of Bozeman).
Yellow dry pea thousand kernel weight (TKW)
TKW’s were collected from five locations and ranged from 227 to 251 grams per thousand kernels (Table 7). Significant differences for entries within a location were observed for all locations examined.
Yellow dry pea test weight
Test weight data was recorded for all locations and location mean test weights ranged from 61.5 lb/bu (Havre) to 65.7 lb/bu (Moccasin) (Table 8). Test weights were considerably lower at Havre than at other locations which all averaged 64-66 lb/bu.
Yellow dry pea plant height
Mean plant heights ranged from 50 cm (Bozeman) to 83 cm (Richland) (Table 9). Multiple varieties averaged more than 90 cm at Richland. The combination of tall plants and heavy pod loads did result in some lodging at Richland creating harvest losses that suppressed the yield of some varieties. Significant differences for entries within a location were observed for all locations except Bozeman.
Yellow dry pea days to flowering
The number of days to flowering were recorded for all trials located at a research center (Table 10). Consistent with previous years Sidney had the shortest mean time to flowering at 54 days and Moccasin the longest at 63 days (Table 10). Time to flowering was 12 days shorter at Moccasin in 2020 relative to 2019.
Green dry pea grain yield
The mean grain yield for green pea ranged from 2276 lb/ac at Broadview to 4353 lb/ac at Huntley under irrigation (Table 11). As with yellow peas, yields were very good at Richland and Havre with yields at Richland exceeding those of the irrigated locations in many instances. Significant differences for entries within a location were observed for all locations except Richland.
Green dry pea protein content
Green peaprotein content is presented in Table 12. The mean protein content by location varied from 22.6% at Sidney to 26% at Bozeman.Average protein contents for green peas are generally higher than that of yellow peas and this was true in 2020 at all locations.Protein contents were also higher in 2020 relative to 2019 at all locations.
Green dry pea thousand kernel weight (TKW)
TKW’s were collected from five locations in 2020 and ranged from 217 to 245 grams per thousand kernels (Table 13). Significant differences for entries within a location were observed for all locations examined.
Green dry pea test weight
Mean test weights for green pea ranged from 61.1 lb/bu to 65.6 lb/bu (Table 14). Test weights were consistent with 2019 results for all locations except Havre which produced lighter test weights in 2020. The differences in test weight among entries were significant within a location for all locations.
Green dry pea plant height
Mean plant heights ranged from 50 cm at Havre to 83 cm at Huntley and Richland (Table 15).
Green dry pea days to flowering
Mean days to flower ranged from 55 days at Sidney to 64 days at Bozeman (Table 16). Time to flowering was 11 days shorter at Moccasin in 2020 relative to 2019, consistent with the trend observed for yellow peas.
Summary
Pea yield and seed protein levels varied greatly amongst locations. Abundant moisture
in May and June resulted in exceptionally high yields at Richland and Havre. Pea yields
at Richland were similar to those at the irrigated locations of Sidney and Huntley.
Interestingly, the Richland site produced these high yields without sacrificing protein
content. Protein contents were nearly identical at Richland between 2019 and 2020
even though yields were considerably greater in 2020 (49% yield increase for yellow
peas and a 60% yield increase for green peas). Furthermore, amongst the varieties
planted in common at the Richland, Sidney (irrigated) and Huntley (irrigated) locations,
the Richland yields rivaled Huntley and generally exceeded Sidney while producing
protein levels definitively higher than either of the irrigated locations. These observations
stress the importance of the growing environment on pea seed protein levels and indicate
that high yields in pea can be achieved without sacrificing protein content.
Table 5. Yellow Dry Pea Grain Yield (lb/a) - 2020 Montana Statewide Variety Evaluation
| Yellow Pea Variety/Line |
Bozeman | Broadview | Havre | Huntley (Irrigated) |
Moccasin | Richland | Sidney (Irrigated) |
| AAC Asher | 5079 | ||||||
| AAC Carver | 3563 | 3210 | 5209 | ||||
| AAC Chrome | 3733 | 5068 | |||||
| AAC Profit | 3363 | ||||||
| AC Agassiz | 3262 | 2856 | 4538 | ||||
| AC Earlystar | 3699 | 3206 | 5151 | ||||
| CDC Amarillo | 3602 | 2768 | 4824 | ||||
| CDC Dakota | 4372 | ||||||
| CDC Inca | 3543 | 2665 | 4742 | ||||
| CDC Saffron | 3444 | 2621 | 4721 | ||||
| CDC Spectrum | 3556 | 2381 | 4647 | ||||
| Delta | 2767 | 2840 | 3356 | 4601 | 2924 | 3674 | 4305 |
| DL Apollo | 3367 | 4847 | |||||
| DS-Admiral | 2730 | 3154 | 3632 | 5022 | 2989 | 4717 | 4468 |
| Durwood | 3195 | 4359 | |||||
| Goldenwood | 3352 | 4029 | |||||
| Hyline | 3444 | 4881 | |||||
| Jetset | 3627 | 3014 | 4759 | ||||
| Korando | 3257 | 4548 | |||||
| LG Amigo | 3529 | 4520 | |||||
| LG Sunrise | 3664 | 4735 | |||||
| Majestic | 4429 | ||||||
| MS-19YP3 | 3698 | 4746 | |||||
| ND Dawn | 2997 | 2734 | 3611 | 4854 | 2917 | 4514 | 4602 |
| Nette 2010 | 3499 | 4831 | |||||
| Orchestra | 5194 | ||||||
| Pro 093-7410 | 3427 | 4865 | |||||
| Pro 133-6243 | 3525 | 4738 | |||||
| Pro 143-6220 | 3458 | 3546 | |||||
| Pro 143-6230 | 3486 | 4266 | |||||
| Pro 153-7409 | 3198 | 3898 | |||||
| PSO877MT632 | 2961 | 2138 | 3277 | 4264 | 2403 | 3901 | 3729 |
| Salamanca | 3474 | 4348 | |||||
| Yellowstone | 3326 | ||||||
| Mean | 2864 | 2717 | 3472 | 4685 | 2830 | 4593 | 4276 |
| P-Value | 0.4335 | 0.0230 | 0.0209 | 0.1932 | 0.0164 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 |
| LSD | NS | 605.9 | 321.9 | NS | 488.2 | 595.0 | 253.6 |
| CV (%) | 9.5 | 14.3 | 6.6 | 10.3 | 12.0 | 9.0 | 3.7 |
Table 6. Yellow Dry Pea Protein (%) - 2020 Montana Statewide Variety Evaluation
| Yellow Pea Variety/Line |
Bozeman | Broadview | Havre | Huntley | Moccasin | Richland | Sidney |
| AAC Asher | 24.0 | ||||||
| AAC Carver | 21.2 | 21.3 | 22.6 | ||||
| AAC Chrome | 21.8 | 23.3 | |||||
| AAC Profit | 22.3 | ||||||
| AC Agassiz | 22.0 | 23.6 | 24.2 | ||||
| AC Earlystar | 21.4 | 23.1 | 22.5 | ||||
| CDC Amarillo | 22.2 | 22.5 | 23.4 | ||||
| CDC Dakota | 26.6 | ||||||
| CDC Inca | 22.5 | 25.5 | 24.5 | ||||
| CDC Saffron | 22.2 | 22.6 | 24.7 | ||||
| CDC Spectrum | 23.0 | 24.8 | 25.0 | ||||
| Delta | 27.3 | 22.7 | 23.2 | 21.4 | 23.9 | 24.5 | 21.3 |
| DL Apollo | 23.0 | 25.0 | |||||
| DS-Admiral | 25.0 | 21.1 | 22.5 | 21.7 | 21.8 | 23.5 | 20.9 |
| Durwood | 22.7 | 24.4 | |||||
| Goldenwood | 23.0 | 26.2 | |||||
| Hyline | 21.6 | 22.8 | |||||
| Jetset | 23.2 | 23.7 | 24.8 | ||||
| Korando | 23.3 | 25.4 | |||||
| LG Amigo | 23.1 | 24.1 | |||||
| LG Sunrise | 21.7 | 23.1 | |||||
| Majestic | 24.6 | ||||||
| MS-19YP3 | 22.1 | 24.2 | |||||
| ND Dawn | 25.0 | 23.7 | 22.1 | 21.5 | 23.8 | 23.2 | 21.3 |
| Nette 2010 | 22.2 | 23.4 | |||||
| Orchestra | 25.8 | ||||||
| Pro 093-7410 | 21.2 | 22.7 | |||||
| Pro 133-6243 | 22.4 | 24.5 | |||||
| Pro 143-6220 | 22.7 | 25.2 | |||||
| Pro 143-6230 | 23.1 | 25.3 | |||||
| Pro 153-7409 | 22.0 | 24.8 | |||||
| PSO877MT632 | 27.0 | 23.6 | 24.0 | 23.5 | 24.9 | 26.0 | 22.6 |
| Salamanca | 22.7 | 24.5 | |||||
| Yellowstone | 22.6 | ||||||
| Mean | 26.1 | 22.7 | 22.4 | 22.0 | 23.4 | 24.3 | 21.5 |
| P-Value | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 |
| LSD | 0.8 | 0.9 | 0.9 | 1.1 | 1.0 | 0.5 | 0.4 |
| CV (%) | 1.9 | 2.7 | 2.9 | 3.4 | 2.9 | 1.4 | 1.2 |
Table 7. Yellow Dry Pea Thousand Kernel Weight (g) - 2020 Montana Statewide Variety Evaluation
| Yellow Pea Variety/Line |
Bozeman | Havre | Moccasin | Richland | Sidney |
| AAC Asher | 274 | ||||
| AAC Carver | 246 | 227 | 247 | ||
| AAC Chrome | 255 | 245 | |||
| AAC Profit | 250 | ||||
| AC Agassiz | 237 | 213 | 248 | ||
| AC Earlystar | 224 | 221 | 228 | ||
| CDC Amarillo | 239 | 215 | 233 | ||
| CDC Dakota | 201 | ||||
| CDC Inca | 238 | 221 | 240 | ||
| CDC Saffron | 255 | 229 | 263 | ||
| CDC Spectrum | 246 | 232 | 249 | ||
| Delta | 249 | 251 | 235 | 258 | 233 |
| DL Apollo | 234 | 240 | |||
| DS-Admiral | 274 | 251 | 241 | 256 | 235 |
| Durwood | 238 | 257 | |||
| Goldenwood | 182 | 183 | |||
| Hyline | 251 | 259 | |||
| Jetset | 250 | 246 | 254 | ||
| Korando | 275 | 285 | |||
| LG Amigo | 240 | 245 | |||
| LG Sunrise | 244 | 248 | |||
| Majestic | 270 | ||||
| MS-19YP3 | 237 | 250 | |||
| ND Dawn | 246 | 251 | 225 | 252 | 235 |
| Nette 2010 | 252 | 252 | |||
| Orchestra | 288 | ||||
| Pro 093-7410 | 230 | 236 | |||
| Pro 133-6243 | 297 | 306 | |||
| Pro 143-6220 | 234 | 232 | |||
| Pro 143-6230 | 225 | 227 | |||
| Pro 153-7409 | 251 | 264 | |||
| PSO877MT632 | 236 | 234 | 221 | 237 | 215 |
| Salamanca | 258 | 276 | |||
| Yellowstone | 293 | ||||
| Mean | 251 | 246 | 227 | 250 | 229 |
| P-Value | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | 0.0001 |
| LSD | 8.7 | 7.8 | 7.5 | 9.0 | 6.6 |
| CV (%) | 2.2 | 2.3 | 2.3 | 2.5 | 1.8 |
Table 8. Yellow Dry Pea Test Weight (lb/bu)
| Yellow Pea Variety/Line |
Bozeman | Broadview | Havre | Huntley | Moccasin | Richland | Sidney Irrigated |
| AAC Asher | 64.6 | ||||||
| AAC Carver | 61.8 | 65.7 | 64.9 | ||||
| AAC Chrome | 61.1 | 64.2 | |||||
| AAC Profit | 60.9 | ||||||
| AC Agassiz | 60.6 | 64.9 | 64.2 | ||||
| AC Earlystar | 61.4 | 65.1 | 64.7 | ||||
| CDC Amarillo | 61.4 | 66.2 | 64.8 | ||||
| CDC Dakota | 66.3 | ||||||
| CDC Inca | 61.3 | 66.2 | 64.9 | ||||
| CDC Saffron | 61.7 | 66.0 | 65.0 | ||||
| CDC Spectrum | 60.7 | 65.8 | 64.3 | ||||
| Delta | 65.1 | 64.7 | 62.2 | 65.6 | 66.4 | 65.0 | 64.8 |
| DL Apollo | 61.8 | 65.2 | |||||
| DS-Admiral | 65.2 | 64.8 | 62.0 | 66.5 | 66.1 | 65.3 | 65.3 |
| Durwood | 61.6 | 64.6 | |||||
| Goldenwood | 62.2 | 64.9 | |||||
| Hyline | 61.3 | 64.8 | |||||
| Jetset | 61.6 | 64.6 | 64.2 | ||||
| Korando | 61.6 | 65.0 | |||||
| LG Amigo | 60.7 | 63.7 | |||||
| LG Sunrise | 61.9 | 65.3 | |||||
| Majestic | 65.0 | ||||||
| MS-19YP3 | 62.8 | 66.4 | |||||
| ND Dawn | 63.3 | 64.0 | 60.6 | 65.3 | 65.0 | 63.8 | 64.5 |
| Nette 2010 | 62.1 | 65.2 | |||||
| Orchestra | 65.0 | ||||||
| Pro 093-7410 | 61.6 | 64.9 | |||||
| Pro 133-6243 | 62.6 | 65.0 | |||||
| Pro 143-6220 | 60.7 | 63.6 | |||||
| Pro 143-6230 | 60.8 | 63.8 | |||||
| Pro 153-7409 | 61.6 | 63.7 | |||||
| PSO877MT632 | 65.2 | 64.6 | 61.5 | 64.6 | 66.1 | 64.8 | 63.3 |
| Salamanca | 61.4 | 64.8 | |||||
| Yellowstone | 62.1 | ||||||
| Mean | 64.7 | 64.5 | 61.5 | 65.5 | 65.7 | 64.7 | 64.5 |
| P-Value | <0.0001 | 0.0409 | <0.0001 | 0.0016 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | 0.001 |
| LSD | 0.4 | 0.5 | 0.6 | 0.8 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.7 |
| CV (%) | 0.4 | 0.5 | 0.6 | 0.7 | 0.5 | 0.6 | 0.7 |
Table 9. Yellow Dry Pea Plant Height (cm)
| Yellow Pea Variety/Line |
Bozeman | Broadview | Havre | Huntley | Moccasin | Richland | Sidney Irrigated |
| AAC Asher | 76 | ||||||
| AAC Carver | 56 | 75 | 86 | ||||
| AAC Chrome | 51 | 82 | |||||
| AAC Profit | 55 | ||||||
| AC Agassiz | 51 | 77 | 78 | ||||
| AC Earlystar | 56 | 82 | 88 | ||||
| CDC Amarillo | 62 | 79 | 91 | ||||
| CDC Dakota | 85 | ||||||
| CDC Inca | 57 | 77 | 93 | ||||
| CDC Saffron | 50 | 65 | 81 | ||||
| CDC Spectrum | 54 | 62 | 83 | ||||
| Delta | 46 | 64 | 39 | 65 | 58 | 80 | 61 |
| DL Apollo | 56 | 89 | |||||
| DS-Admiral | 52 | 73 | 52 | 81 | 71 | 85 | 71 |
| Durwood | 61 | 89 | |||||
| Goldenwood | 43 | 70 | |||||
| Hyline | 51 | 80 | |||||
| Jetset | 55 | 70 | 84 | ||||
| Korando | 52 | 81 | |||||
| LG Amigo | 48 | 77 | |||||
| LG Sunrise | 60 | 93 | |||||
| Majestic | 88 | ||||||
| MS-19YP3 | 54 | 86 | |||||
| ND Dawn | 52 | 64 | 47 | 76 | 71 | 81 | 73 |
| Nette 2010 | 54 | 79 | |||||
| Orchestra | 93 | ||||||
| Pro 093-7410 | 48 | 85 | |||||
| Pro 133-6243 | 46 | 81 | |||||
| Pro 143-6220 | 49 | 79 | |||||
| Pro 143-6230 | 48 | 81 | |||||
| Pro 153-7409 | 46 | 76 | |||||
| PSO877MT632 | 52 | 71 | 39 | 80 | 62 | 75 | 61 |
| Salamanca | 55 | 86 | |||||
| Yellowstone | 46 | ||||||
| Mean | 50 | 68 | 51 | 75 | 71 | 83 | 67 |
| P-Value | 0.5391 | 0.1983 | <0.0001 | 0.0005 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | 0.0004 |
| LSD | NS | NS | 6.3 | 6.2 | 6.5 | 9.3 | 4.6 |
| CV (%) | 14.1 | 10.0 | 8.7 | 5.3 | 6.4 | 7.8 | 4.3 |
Table 10. Yellow Dry Pea Days to Flowering
| Yellow Pea Variety/Line |
Bozeman | Havre | Huntley | Moccasin | Sidney Irrigated |
| AAC Asher | |||||
| AAC Carver | 58 | 64 | |||
| AAC Chrome | 58 | ||||
| AAC Profit | 59 | ||||
| AC Agassiz | 58 | 63 | |||
| AC Earlystar | 56 | 63 | |||
| CDC Amarillo | 61 | 65 | |||
| CDC Dakota | |||||
| CDC Inca | 59 | 64 | |||
| CDC Saffron | 59 | 65 | |||
| CDC Spectrum | 59 | 65 | |||
| Delta | 62 | 53 | 57 | 62 | 53 |
| DL Apollo | 57 | ||||
| DS-Admiral | 63 | 55 | 57 | 62 | 53 |
| Durwood | 57 | ||||
| Goldenwood | 63 | ||||
| Hyline | 58 | ||||
| Jetset | 57 | 63 | |||
| Korando | 53 | ||||
| LG Amigo | 57 | ||||
| LG Sunrise | 53 | ||||
| Majestic | |||||
| MS-19YP3 | 54 | ||||
| ND Dawn | 64 | 58 | 60 | 64 | 54 |
| Nette 2010 | 54 | ||||
| Orchestra | |||||
| Pro 093-7410 | 55 | ||||
| Pro 133-6243 | 53 | ||||
| Pro 143-6220 | 58 | ||||
| Pro 143-6230 | 57 | ||||
| Pro 153-7409 | 53 | ||||
| PSO877MT632 | 63 | 55 | 58 | 63 | 54 |
| Salamanca | 55 | ||||
| Yellowstone | 53 | ||||
| Mean | 63 | 56 | 58 | 63 | 54 |
| P-Value | 0.1596 | <0.0001 | 0.0242 | <0.0001 | 0.0080 |
| LSD | NS | 1.3 | 2.5 | 0.8 | 0.5 |
| CV (%) | 1.1 | 1.6 | 2.8 | 0.9 | 0.6 |
Table 11. Green Dry Pea Grain Yield (lb/ac)
| Green Pea Variety/Line |
Bozeman | Broadview | Havre | Huntley | Moccasin | Richland | Sidney Irrigated |
| AAC Comfort | 3566 | 4815 | |||||
| Aragorn | 2538 | 2621 | 3184 | 4114 | 2632 | 3886 | 3926 |
| Bluemoon | 4194 | ||||||
| CDC Greenwater | 3325 | 4333 | |||||
| CDC Striker | 1348 | 1267 | 3503 | 3887 | 2414 | 4018 | 3864 |
| Daytona | 3333 | 4867 | |||||
| Empire | 3555 | 4277 | |||||
| Fairway | 3606 | ||||||
| Ginny 2 | 3534 | 4031 | |||||
| Hampton | 2692 | 2312 | 3324 | 4781 | 2608 | 4773 | 4368 |
| Majoret | 1758 | 1657 | 3754 | 4191 | 2628 | 3962 | 4024 |
| NDP100144G | 3107 | 1969 | 3449 | 4313 | 2294 | 4469 | 4063 |
| NDP160028 | 3061 | 2979 | 3401 | 5007 | 3112 | 4548 | 4667 |
| Pro 141-6258 | 3784 | 4043 | |||||
| Pro 171-7665 | 3688 | ||||||
| PSO877MT457 | 2535 | 3123 | 3151 | 4179 | 2780 | 4252 | 3837 |
| Shamrock | 3591 | 4204 | |||||
| Mean | 2434 | 2276 | 3484 | 4353 | 2638 | 4300 | 4107 |
| P-Value | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | 0.0019 | 0.0437 | 0.0490 | 0.1 | <0.0001 |
| LSD | 441.4 | 398.8 | 306.8 | 711.9 | 479.9 | NS | 280.1 |
| CV (%) | 12.3 | 11.9 | 6.2 | 11.1 | 12.3 | 10.9 | 4.6 |
Table 12. Green Dry Pea Protein* (%)
| Green Pea Variety/Line |
Bozeman | Broadview | Havre | Huntley | Moccasin | Richland | Sidney Irrigated |
| AAC Comfort | 23.1 | 24.1 | |||||
| Aragorn | 25.7 | 23.0 | 23.0 | 24.1 | 23.5 | 24.8 | 22.6 |
| Bluemoon | 24.4 | ||||||
| CDC Greenwater | 22.4 | 23.6 | |||||
| CDC Striker | 27.0 | 25.4 | 23.7 | 24.3 | 24.3 | 25.2 | 22.5 |
| Daytona | 22.7 | 23.9 | |||||
| Empire | 23.3 | 24.8 | |||||
| Fairway | 23.4 | ||||||
| Ginny 2 | 22.1 | 25.1 | |||||
| Hampton | 27.6 | 25.1 | 24.2 | 23.5 | 23.7 | 25.4 | 22.3 |
| Majoret | 27.0 | 24.5 | 23.8 | 23.1 | 24.7 | 25.4 | 22.3 |
| NDP100144G | 25.4 | 24.7 | 23.3 | 23.2 | 24.7 | 24.9 | 22.8 |
| NDP160028 | 24.7 | 24.2 | 22.2 | 22.4 | 23.6 | 24.1 | 21.6 |
| Pro 141-6258 | 21.5 | 24.4 | |||||
| Pro 171-7665 | 21.5 | ||||||
| PSO877MT457 | 27.5 | 25.1 | 24.5 | 25.9 | 24.3 | 26.1 | 24.2 |
| Shamrock | 22.6 | 23.8 | |||||
| Mean | 26 | 24.6 | 22.9 | 23.8 | 24.1 | 24.7 | 22.6 |
| P-Value | <0.0001 | 0.0012 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | 0.0117 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 |
| LSD | 0.9 | 1.0 | 0.9 | 1.0 | 0.8 | 0.6 | 0.6 |
| CV (%) | 2.2 | 2.7 | 2.8 | 2.9 | 2.2 | 1.5 | 1.9 |
Table 13. Green Dry Pea Thousand Kernel Weight (g)
| Green Pea Variety/Line |
Bozeman | Havre | Moccasin | Richland | Sidney Irrigated |
| AAC Comfort | 278 | 269 | |||
| Aragorn | 230 | 224 | 217 | 236 | 201 |
| Bluemoon | 264 | ||||
| CDC Greenwater | 239 | 244 | |||
| CDC Striker | 241 | 253 | 230 | 251 | 238 |
| Daytona | 274 | 279 | |||
| Empire | 229 | 232 | |||
| Fairway | 200 | ||||
| Ginny 2 | 230 | 244 | |||
| Hampton | 232 | 237 | 219 | 239 | 217 |
| Majoret | 236 | 242 | 225 | 248 | 229 |
| NDP100144G | 214 | 211 | 193 | 198 | 196 |
| NDP160028 | 201 | 221 | 206 | 235 | 216 |
| Pro 141-6258 | 227 | 233 | |||
| Pro 171-7665 | 247 | ||||
| PSO877MT457 | 252 | 249 | 241 | 253 | 224 |
| Shamrock | 254 | 250 | |||
| Mean | 229 | 238 | 219 | 245 | 217 |
| P-Value | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 |
| LSD | 4.7 | 6.8 | 10.5 | 8.6 | 6.4 |
| CV (%) | 1.4 | 2.0 | 3.3 | 2.4 | 2.0 |
Table 14. Green Dry Pea Test Weight (lb/bu)
| Green Pea Variety/Line |
Bozeman | Broadview | Havre | Huntley | Moccasin | Richland | Sidney Irrigated |
| AAC Comfort | 60.3 | 64.4 | |||||
| Aragorn | 62.3 | 63.8 | 60.4 | 65.1 | 63.7 | 63.2 | 62.9 |
| Bluemoon | 64.1 | ||||||
| CDC Greenwater | 60.9 | 64.8 | |||||
| CDC Striker | 64.3 | 64.7 | 61.5 | 65.1 | 66.5 | 64.8 | 65.1 |
| Daytona | 61.2 | 64.3 | |||||
| Empire | 61.5 | 66.3 | |||||
| Fairway | 60.3 | ||||||
| Ginny 2 | 61.1 | 63.7 | |||||
| Hampton | 63.3 | 64.2 | 60.3 | 65.0 | 65.5 | 63.5 | 63.6 |
| Majoret | 64.4 | 64.8 | 61.3 | 65.1 | 66.6 | 64.5 | 65.8 |
| NDP100144G | 64.1 | 64.0 | 61.0 | 64.4 | 65.1 | 63.8 | 64.3 |
| NDP160028 | 66.2 | 65.9 | 61.9 | 65.9 | 67.1 | 66.3 | 66.0 |
| Pro 141-6258 | 61.6 | 64.6 | |||||
| Pro 171-7665 | 62.0 | ||||||
| PSO877MT457 | 63.6 | 63.9 | 61.0 | 64.4 | 65.0 | 63.6 | 63.3 |
| Shamrock | 61.6 | 66.3 | |||||
| Mean | 64.0 | 64.5 | 61.1 | 65.0 | 65.6 | 64.6 | 64.4 |
| P-Value | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | 0.0774 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | 0.0007 |
| LSD | 0.6 | 0.4 | 0.6 | 1.0 | 0.4 | 0.6 | 1.4 |
| CV (%) | 0.6 | 0.4 | 0.7 | 1.0 | 0.4 | 0.6 | 1.5 |
Table 15. Green Dry Pea Plant Height (cm)
| Green Pea Variety/Line |
Bozeman | Broadview | Havre | Huntley | Moccasin | Richland | Sidney Irrigated |
| AAC Comfort | 49 | 90 | |||||
| Aragorn | 44 | 73 | 42 | 74 | 67 | 75 | 64 |
| Bluemoon | 78 | ||||||
| CDC Greenwater | 54 | 91 | |||||
| CDC Striker | 56 | 68 | 52 | 77 | 69 | 87 | 65 |
| Daytona | 42 | 80 | |||||
| Empire | 71 | 94 | |||||
| Fairway | 47 | ||||||
| Ginny 2 | 49 | 74 | |||||
| Hampton | 43 | 63 | 42 | 73 | 64 | 70 | 62 |
| Majoret | 60 | 67 | 48 | 79 | 68 | 80 | 67 |
| NDP100144G | 68 | 90 | 61 | 106 | 87 | 93 | 71 |
| NDP160028 | 49 | 72 | 58 | 83 | 74 | 82 | 69 |
| Pro 141-6258 | 39 | 73 | |||||
| Pro 171-7665 | 46 | ||||||
| PSO877MT457 | 48 | 70 | 47 | 92 | 80 | 87 | 70 |
| Shamrock | 54 | 90 | |||||
| Mean | 53 | 72 | 50 | 83 | 73 | 83 | 67 |
| P-Value | 0.001 | 0.0005 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | 0.0001 | <0.0001 | 0.1 |
| LSD | 11.2 | 9.7 | 5.2 | 8.0 | 8.4 | 9.7 | NS |
| CV (%) | 14.4 | 9.2 | 7.3 | 6.5 | 7.9 | 7.9 | 7.0 |
Table 16. Green Dry Pea Days to Flowering
| Green Pea Variety/Line |
Bozeman | Havre | Huntley | Moccasin | Sidney Irrigated |
| AAC Comfort | 62 | ||||
| Aragorn | 61 | 53 | 55 | 62 | 53 |
| Bluemoon | |||||
| CDC Greenwater | 60 | ||||
| CDC Striker | 64 | 59 | 61 | 64 | 57 |
| Daytona | 57 | ||||
| Empire | 60 | ||||
| Fairway | 59 | ||||
| Ginny 2 | 56 | ||||
| Hampton | 65 | 58 | 60 | 63 | 54 |
| Majoret | 63 | 59 | 59 | 64 | 55 |
| NDP100144G | 69 | 61 | 62 | 66 | 57 |
| NDP160028 | 66 | 59 | 60 | 64 | 56 |
| Pro 141-6258 | 53 | ||||
| Pro 171-7665 | 54 | ||||
| PSO877MT457 | 63 | 53 | 52 | 61 | 52 |
| Shamrock | 60 | ||||
| Mean | 64 | 58 | 58 | 63 | 55 |
| P-Value | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 |
| LSD | 2.9 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 0.8 | 1.4 |
| CV (%) | 3.1 | 1.3 | 1.3 | 0.9 | 1.7 |
Lentil Variety Evaluation in 2020
A total of 13 lentil entries were evaluated at six locations with nine entries tested at all locations. One additional dryland location at Huntley was lost to grasshoppers prior to harvest.
Lentil grain yield
The mean grain yield varied from 1202 lb/ac to 3181 lb/ac (Table 17). The differences in grain yield among entries within a location was significant for five of the seven locations. The Richland location had an average yield greater than any year dating back to 2011 and the Havre location recorded its 2nd highest average lentil yield over the same time span. The variety Avondale was the highest yielding variety at Richland and produced the highest yield recorded for any lentil variety in the past ten years of this trial within the locations tested this year.
Lentil TKW
Thousand kernel weights (TKW) were obtained for all entries at five locations (Table 18). The mean TKW ranged from 40.3 g per 1000 seeds at Havre to 48.9 g per 1000 seeds recorded at Sidney.TKWs were significantly different for different classes of lentils within a location for all locations.
Lentil test weight
The mean test weight ranged from 59.8 lb/bu at Moccasin to 64.1 lb/bu at Richland (Table 19). The test weight differences among entries within a location were significant for all locations.
Lentil plant height
The mean plant height ranged from 28 cm at Moccasin to 43 cm at Huntley (Table 20). Plant height differences among entries within a location were only significant for two locations.
Lentil number of days to flowering
The mean number of days to flowering ranging from 55 days at Sidney to 63 days recorded at three locations (Table 21). In 2020, the days to flowering interval was shorter than that observed for 2019 but consistent with prior years.
Table 17. Lentil Grain Yield (lb/a)
| Lentil Variety/Line |
Bozeman | Havre | Huntley Irrigated |
Moccasin | Richland | Sidney Irrigated |
| Avondale | 2306 | 2685 | 1441 | 2060 | 3433 | 3332 |
| CDC Greenstar | 2265 | 2813 | ||||
| CDC Impala CL | 2573 | 2007 | 1397 | 1794 | 2923 | 3182 |
| CDC Impress CL | 2331 | 2458 | 1257 | 1792 | 2712 | 3031 |
| CDC Imvincible CL | 2896 | |||||
| CDC Kermit | 2169 | 3151 | ||||
| CDC Maxim CL | 3102 | |||||
| CDC Richlea | 2880 | 2613 | 1061 | 1850 | 3189 | 3210 |
| CDC Viceroy | 1780 | 2150 | 1367 | 1957 | 2840 | 3230 |
| NDL090170L | 2029 | 2553 | 928 | 1623 | 2735 | 2860 |
| NDL090185R | 2491 | 2683 | 1010 | 1825 | 3338 | 3259 |
| NDL120600R | 2122 | 2096 | 1139 | 2004 | 2412 | 2887 |
| Sage | 2329 | 2261 | 1220 | 2280 | 3139 | 3638 |
| Mean | 2316 | 2358 | 1202 | 1909 | 2976 | 3181 |
| P-Value | 0.181 | <0.0001 | 0.5662 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | 0.0010 |
| LSD | NS | 208.4 | NS | 163.6 | 304.6 | 312.1 |
| CV (%) | 22.1 | 6.1 | 32.5 | 5.9 | 7.1 | 6.7 |
Table 18. Lentil Thousand Kernel Weight (g)
| Lentil Variety/Line |
Bozeman | Havre | Moccasin | Richland | Sidney Irrigated |
| Avondale | 50.8 | 44.2 | 46.8 | 46.9 | 48.7 |
| CDC Greenstar | 58.5 | 65.3 | |||
| CDC Impala CL | 29.6 | 24.8 | 26.8 | 25.9 | 31.7 |
| CDC Impress CL | 51.5 | 43.8 | 46.0 | 47.0 | 55.3 |
| CDC Imvincible CL | 28.3 | ||||
| CDC Kermit | 24.3 | 26.2 | |||
| CDC Maxim CL | 36.1 | ||||
| CDC Richlea | 52.4 | 45.1 | 48.4 | 49.2 | 51.3 |
| CDC Viceroy | 32.9 | 27.0 | 28.6 | 29.0 | 34.6 |
| NDL090170L | 61.6 | 58.3 | 59.5 | 64.2 | 74.3 |
| NDL090185R | 51.6 | 39.5 | 45.1 | 45.3 | 52.4 |
| NDL120600R | 52.4 | 44.1 | 48.6 | 50.5 | 55.0 |
| Sage | 39.5 | 33.2 | 32.8 | 35.3 | 36.8 |
| Mean | 46.9 | 40.3 | 42.5 | 42.2 | 48.9 |
| P-Value | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 |
| LSD | 4.2 | 1.9 | 1.7 | 1.8 | 1.3 |
| CV (%) | 6.2 | 3.2 | 2.7 | 3.1 | 1.8 |
Table 19. Lentil Test Weight (lb/bu)
| Lentil Variety/Line |
Bozeman | Havre | Huntley Irrigated |
Moccasin | Richland | Sidney Irrigated |
| Avondale | 62.8 | 62.8 | 60.2 | 61.9 | 63.7 | 62.3 |
| CDC Greenstar | 60.1 | 61.2 | ||||
| CDC Impala CL | 66.1 | 65.9 | 61.7 | 65.3 | 66.4 | 64.9 |
| CDC Impress CL | 62.6 | 62.7 | 59.1 | 61.3 | 63.2 | 62.2 |
| CDC Imvincible CL | 65.6 | |||||
| CDC Kermit | 65.3 | 66.3 | ||||
| CDC Maxim CL | 65.3 | |||||
| CDC Richlea | 62.0 | 61.8 | 58.1 | 60.9 | 62.7 | 61.1 |
| CDC Viceroy | 65.5 | 65.2 | 63.1 | 64.6 | 65.8 | 64.4 |
| NDL090170L | 61.0 | 61.0 | 57.3 | 59.7 | 61.9 | 60.0 |
| NDL 090185R | 63.2 | 62.9 | 59.8 | 62.0 | 63.5 | 61.8 |
| NDL 120600R | 61.9 | 61.7 | 58.7 | 60.5 | 62.3 | 61.0 |
| Sage | 65.0 | 65.1 | 60.6 | 63.9 | 65.7 | 64.0 |
| Mean | 63 | 63.1 | 59.8 | 62.2 | 64.1 | 62.4 |
| P-Value | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | 0.0004 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 |
| LSD | 0.4 | 0.3 | 2.3 | 0.3 | 0.4 | 0.3 |
| CV (%) | 0.4 | 0.4 | 2.6 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.4 |
Table 20. Lentil Plant Height (cm)
| Lentil Variety/Line |
Bozeman | Havre | Huntley Irrigated |
Moccasin | Richland | Sidney Irrigated |
| Avondale | 41 | 34 | 40 | 27 | 40 | 39 |
| CDC Greenstar | 36 | 40 | ||||
| CDC Impala CL | 36 | 30 | 44 | 28 | 41 | 40 |
| CDC Impress CL | 40 | 33 | 43 | 24 | 37 | 42 |
| CDC Imvincible CL | 41 | |||||
| CDC Kermit | 28 | 36 | ||||
| CDC Maxim CL | 40 | |||||
| CDC Richlea | 42 | 33 | 44 | 25 | 40 | 39 |
| CDC Viceroy | 36 | 32 | 44 | 30 | 39 | 39 |
| NDL090170L | 39 | 33 | 44 | 23 | 41 | 40 |
| NDL 090185R | 40 | 32 | 43 | 29 | 43 | 41 |
| NDL 120600R | 40 | 35 | 44 | 31 | 38 | 43 |
| Sage | 38 | 27 | 45 | 35 | 35 | 38 |
| Mean | 41 | 32 | 43 | 28 | 39 | 40 |
| P-Value | 0.7319 | <0.0001 | 0.7051 | <0.0001 | 0.4 | 0.48 |
| LSD | NS | 2.4 | NS | 3.6 | NS | NS |
| CV (%) | 13.2 | 5.3 | 8.6 | 9.0 | 5.9 | 8.1 |
Table 21. Lentil Days to Flowering
| Lentil Variety/Line |
Bozeman | Havre | Huntley Irrigated |
Moccasin | Sidney Irrigated |
| Avondale | 63 | 57 | 63 | 62 | 54 |
| CDC Greenstar | 59 | ||||
| CDC Impala CL | 66 | 59 | 64 | 65 | 60 |
| CDC Impress CL | 64 | 59 | 64 | 65 | 55 |
| CDC Imvincible CL | |||||
| CDC Kermit | 61 | ||||
| CDC Maxim CL | |||||
| CDC Richlea | 64 | 58 | 63 | 63 | 56 |
| CDC Viceroy | 66 | 61 | 64 | 64 | 56 |
| NDL090170L | 62 | 54 | 63 | 62 | 54 |
| NDL 090185R | 64 | 58 | 63 | 64 | 54 |
| NDL 120600R | 61 | 55 | 64 | 61 | 54 |
| Sage | 60 | 55 | 64 | 61 | 54 |
| Mean | 63 | 58 | 63 | 63 | 55 |
| P-Value | 0.002 | <0.0001 | 0.5326 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 |
| LSD | 2.9 | 1.2 | 1.6 | 0.7 | 1.4 |
| CV (%) | 3.1 | 1.5 | 0.7 | 0.8 | 1.7 |
Chickpea Variety Evaluation in 2020
The 2020 statewide chickpea variety evaluation included eleven varieties (ten Kabuli type and one Desi type). Results are reported for six locations. Ascochyta pressure was minimal at the irrigated Sidney location requiring only two fungicide applications as opposed to the normal three or more applications. Yields in Sidney were exceptional, especially for varieties CDC Frontier and CDC Orion. Conversely, four of the locations (Havre, Huntley, Mocassin and Richland) experienced high Ascochyta pressure due to favorable environmental conditions through the central and northern part of the state throughout the summer months. As a result, yields for those variaties lacking Ascochyta resistance are very poor at those locations. The trials at Richland also suffered deer damage which often is variety specific. Mean grain yields ranged from 864 lb/ac at Mocassin to 4497 lb/ac at Sidney and differences in mean grain yield amongst varieties were significant for all locations.
Seed size was evaluated for five locations using a sieve with 8.73 mm (22/64 in) diameter round openings (Table 23). Consistent with 2019, Bozeman had the highest percentage of seeds larger than 8.73 mm in diameter with a site average of 81%.The reduced disease pressure in 2020 at the Sidney location resulted in an increase inpercentage of seeds larger than 8.73 mm in diameter relative to 2019 (39.1% in 2019 to 66.2% in 2020). As expected, the percentage of seed larger than 8.73 mm varied greatly among the varieties.
Table 22. Chickpea Grain yield (lb/a) with Three Year Averages in parentheses
| Chickpea Variety/Line |
Bozeman | Havre | Huntley Dryland |
Moccasin | Richland | Sidney Irrigated |
| CDC Frontier | 4215 | 2335 | 1932 | 1192 | 2244 | 5539 |
| CDC Leader | 2443 | 2793 | ||||
| CDC Orion | 4179 | 2552 | 2163 | 1277 | 2714 | 5590 |
| CDC Palmer | 2446 | 2714 | ||||
| Kasin | 1739 | 1119 | ||||
| Myles | 3000 | 2175 | 1785 | 1419 | 2301 | 3226 |
| Nash | 3807 | 428 | 1148 | 106 | 719 | 4359 |
| ND Crown | 3668 | 2188 | 1797 | 1388 | 1358 | 4738 |
| Royal | 3580 | 552 | 1403 | 236 | 809 | 4380 |
| Sawyer | 3477 | 2006 | 1640 | 1076 | 1819 | 4252 |
| Sierra | 2970 | 674 | 1094 | 217 | 787 | 3888 |
| Mean | 3612 | 1776 | 1620 | 864 | 1742 | 4497 |
| P-Value | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 |
| LSD | 483.1 | 225.7 | 314.3 | 239.5 | 533.9 | 384.2 |
| CV (%) | 9.1 | 8.8 | 13.3 | 18.9 | 20.9 | 5.8 |
Table 23. Chickpea Seed Size (% greater than 8.73 mm)
| Chickpea Variety/Line |
Bozeman | Havre | Moccasin | Richland | Sidney Irrigated |
| CDC Frontier | 77.0 | 8.9 | 19.8 | 17.3 | 47.0 |
| CDC Leader | 21.2 | 36.3 | |||
| CDC Orion | 94.4 | 41.7 | 56.2 | 63.1 | 79.1 |
| CDC Palmer | 26.3 | 60.6 | |||
| Kasin | 1.2 | 2.3 | |||
| Myles | 0.2 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| Nash | 99.2 | 65.4 | 85.4 | 82.1 | 90.4 |
| ND Crown | 88.4 | 40.3 | 59.1 | 66.1 | 76.7 |
| Royal | 98.8 | 70.2 | 85.0 | 82.9 | 88.7 |
| Sawyer | 90.8 | 20.2 | 60.0 | 45.5 | 60.1 |
| Sierra | 98.9 | 60.3 | 71.7 | 83.8 | 87.8 |
| Mean | 80.9 | 32.3 | 54.7 | 49.1 | 66.2 |
| P-Value | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 |
| LSD | 3.4 | 11.6 | 8.1 | 7.7 | 5.9 |
| CV (%) | 2.9 | 24.9 | 10.1 | 10.9 | 6.1 |
FUTURE PLANS
The EARC will continue to lead the statewide variety evaluations in the coming years as long as there is a need from pulse growers, seed industries, breeders, and there is funding to support the effort.
Note: The data and summaries presented in this report are for informational purposes only. Inclusion and or exclusion of any commercial variety in this summary does not constitute a recommendation by Montana State University Agricultural Experiment Station or EARC.
DISCLAIMER:
The information given herein is supplied with the understanding that no discrimination is intended and no endorsement by the Montana Agricultural Experiment Station is implied. The results of individual trials and studies are considered to be of a PRELIMINARY nature and should NOT be considered as a product endorsement or recommendation for commercial use.
Resistance of Pea Varieties to Rhizoctonia Root Rot - Sidney, MT
OBJECTIVE: Test the resistance of different pea varieties to R. solani. (Frankie Crutcher, Amber Ferda and Kevin McPhee)
MATERIALS AND METHODS:
Not Irrigated
Variety: Misc.
Location: Sidney, MT
Planted: 4/30/2020
Harvested: 8/3/2020
Plot Size: 5’ x 20’
Seeding Rate: 8 LS/ft²
Soil Type: Savage silty clay loam
Previous Crop: Wheat
Residual Soil N to 3 ft: 30.2 lbs/A
Residual Soil P to 6 in: 20 ppm
Applied Fertilizer: None
Irrigated (sprinkler): None
Chemical Applications: Outlook 20 fl oz/A, Roundup 20 fl oz/A, Varisto 18 fl oz/A
Precipitation April – September: 8.1 inches
Vigor and stand counts: 5/19/2020, 6/1/2020, 6/19/2020
Root disease assessment: 6/15/2020
COMMENTS: Seeds were inoculated with peat-based commercial Rhizobium N-Charge® (Verdesian Life Sciences, Cary, NC). R. solani AG 2-2 isolate R9 grown on barley was used to inoculate plots at planting. Seed was treated with Cruiser 5FS (1.28 fl oz/cwt) + Apron XL (0.64 fl oz/cwt). Powdery mildew was observed on some varieties close to harvest. Root assessments were done on 6/15/2020. Foliar height and biomass were taken during this time as well.
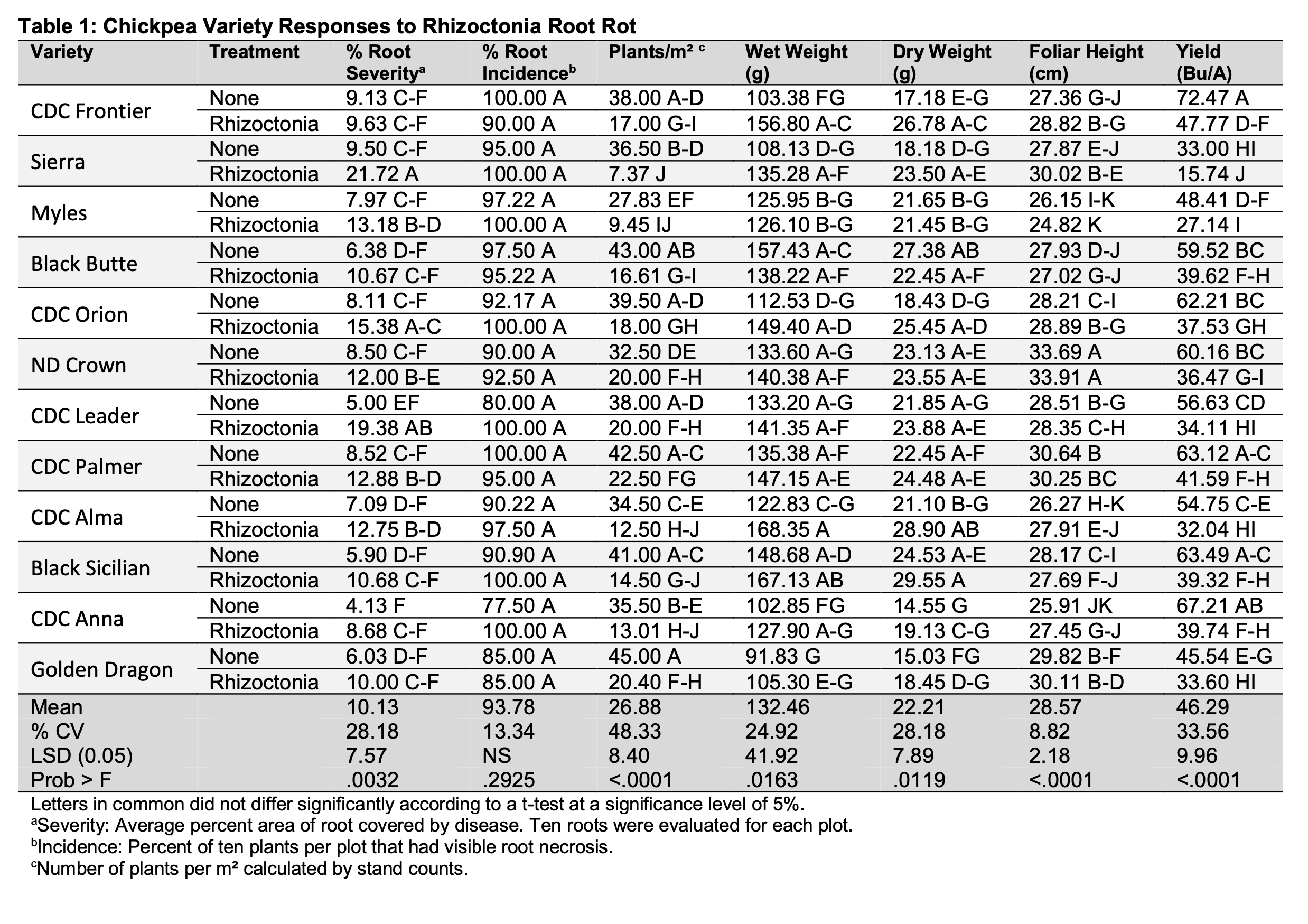
RESULTS: Significant differences were found for root severity, with the treatments containing Rhizoctonia having higher numbers than their counterparts without Rhizoctonia. Significant differences were also found for all other categories except root severity. Aragorn and Greenwood were excluded from the yield analysis, due to lodging and shattering before harvest.
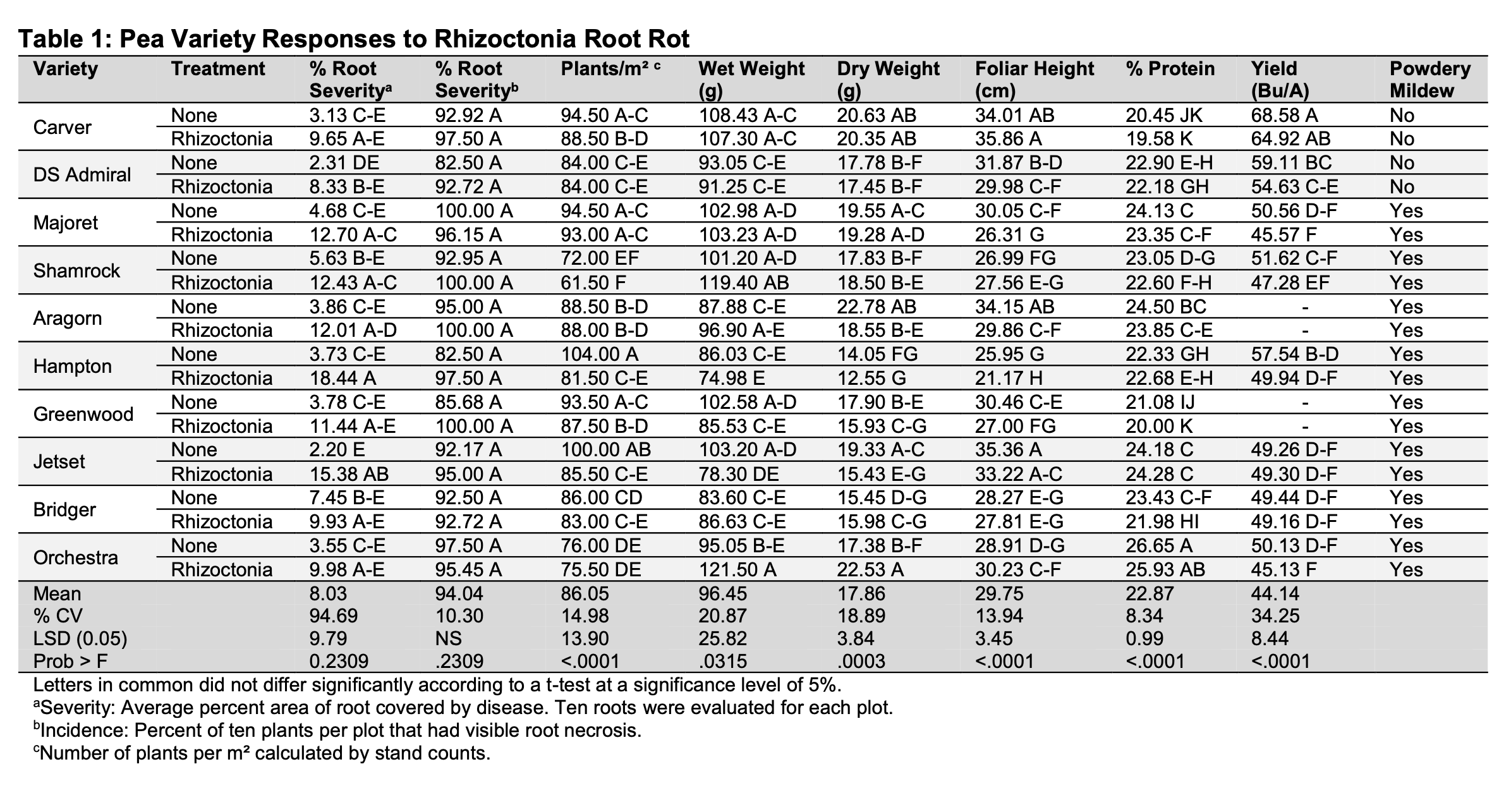
Resistance of Lentil Varieties to Rhizoctonia Root Rot - Sidney, MT
OBJECTIVE: Test the resistance of different lentil varieties to R. solani. (Frankie Crutcher, Amber Ferda and Kevin McPhee)
MATERIALS AND METHODS:
Not Irrigated
Variety: Misc.
Location: Sidney, MT
Planted: 4/30/2020
Harvested: 8/5/2020
Plot Size: 5’ x 20’
Seeding Rate: 12 LS/ft²
Soil Type: Savage silty clay loam
Previous Crop: Wheat
Residual Soil N to 3 ft: 30.2 lbs/A
Residual Soil P to 6 in: 20 ppm
Applied Fertilizer: None
Irrigated (sprinkler): None
Chemical Applications: Outlook 20 fl oz/A, Roundup 20 fl oz/A
Precipitation April – September: 8.1 inches
Vigor and stand counts: 5/19/2020, 6/1/2020, 6/19/2020
Root disease assessment: 6/15/2020
COMMENTS: Seeds were inoculated with peat-based commercial Rhizobium N-Charge® (Verdesian Life Sciences, Cary, NC). R. solani AG 2-2 isolate R9 grown on barley was used to inoculate plots at planting. Seed was treated withCruiser 5FS (1.28 fl oz/cwt) + Apron XL (0.64 fl oz/cwt). Root assessments were done on 6/15/2020. Foliar height and biomass were taken during this time as well.
RESULTS: Significant differences were found for both root severity and root incidence, with the Rhizoctonia treatments showing more root rot than their counterparts without Rhizoctonia. Significant differences were also found for plants/m2. The treatments that contained no Rhizoctonia had higher counts than the treatments with Rhizoctonia. The varieties Richlea, Viceroy, Avondale and Pennell had early pod shattering, which resulted in yield loss and were excluded from analysis for this reason.
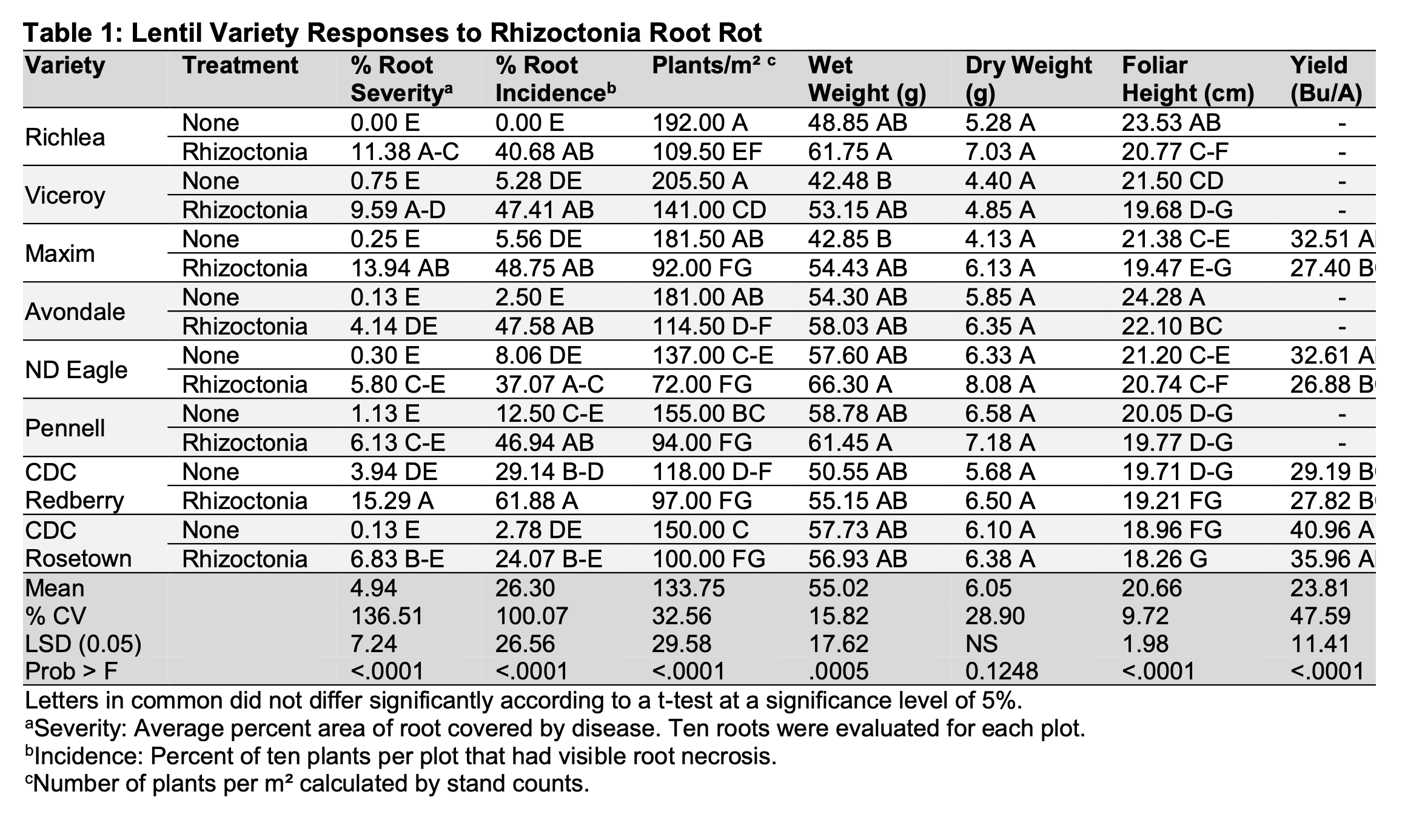
Resistance of Chickpea Varieties to Rhizoctonia Root Rot - Sidney, MT
OBJECTIVE: Test the resistance of different chickpea varieties to R. solani. (Frankie Crutcher, Amber Ferda and Kevin McPhee)
MATERIALS AND METHODS:
Not Irrigated
Variety: Misc.
Location: Sidney, MT
Planted: 4/30/2020
Harvested: 9/4/2020
Plot Size: 5’ x 20’
Seeding Rate: 4 LS/ft²
Soil Type: Savage silty clay loam
Previous Crop: Wheat
Residual Soil N to 3 ft: 30.2 lbs/A
Residual Soil P to 6 in: 20 ppm
Applied Fertilizer: None
Irrigated (sprinkler): None
Chemical Applications: Outlook 20 fl oz/A, Roundup 20 fl oz/A, Tough 5 EC 1 pt/A
Precipitation April – September: 8.1 inches
Vigor and stand counts: 5/19/2020, 6/1/2020, 6/19/2020
Root disease assessment: 6/15/2020
COMMENTS: Seeds were inoculated with peat-based commercial Rhizobium N-Charge® (Verdesian Life Sciences, Cary, NC). R. solani AG 2-2 isolate R9 grown on barley was used to inoculate plots at planting. Seed was treated withCruiser 5FS (1.28 fl oz/cwt) + Apron XL (0.64 fl oz/cwt). Root assessments were done on 6/15/2020. Foliar height and biomass were taken during this time as well.Trial was desiccated with Gramoxone (32 fl oz/A) on 08/24/2020.
RESULTS: Significant differences were found for root severity, with the susceptible control variety Sierra having the highest root severity for both treatments. There were also significant differences for plants/m2 for all of the varieties compared to each treatment. The treatments without Rhizoctonia had a higher plants/m2 than their counterparts with Rhizoctonia. Yield also showed significant differences. The treatments without Rhizoctonia yielded better than those with Rhizoctonia. Sierra had the lowest yield for both treatments, while Frontier yielded the best.