Wheat Midge
Overview
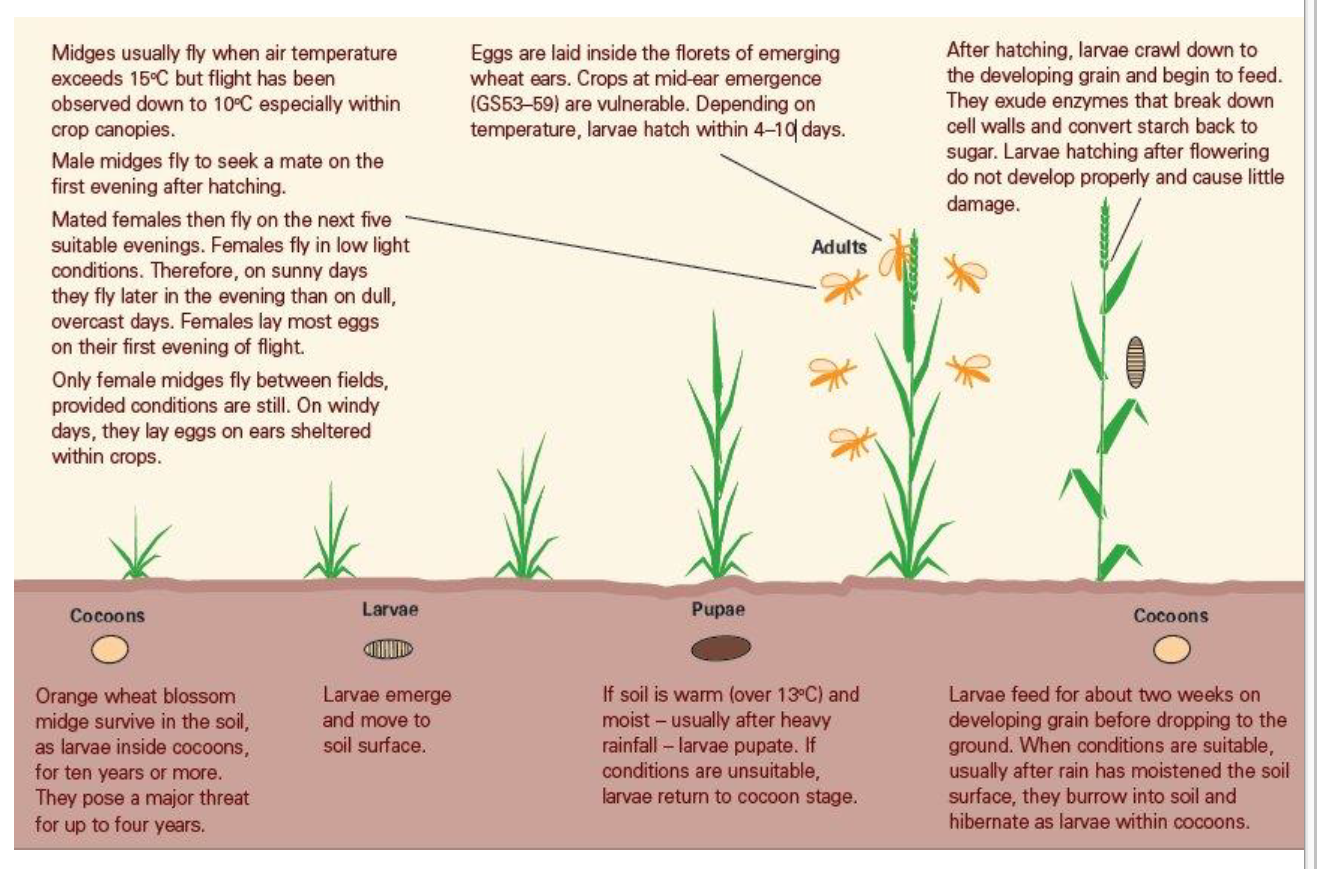
The wheat midge had a huge impact on spring wheat growers in Flathead County during the 2006 growing season, with losses estimated to be nearly $1.5 million. Since 2006, MSU Extension agents have monitored for the presence of this pest in the Golden Triangle area. Midge counts were low or non-existent until 2012, when high numbers were recorded near Valier, MT. In response, MSU Research Center staff and county agents across the state increased monitoring activities. 2014 and 2015 monitoring data is available on the Pestweb site.
Threshold Levels
Phermomone traps give an early warning system. Insecticide treatments are recommended if one or more adults (typically females) ar observed for every six heads when observed at dusk.
Control
Synthetic pyrethroid insecticides are available for control of wheat midge. Control is for actively flying adults based on threshold levels in the crop. Midges are most vulnerable in the evening when actively flying. Avoid treatment after peak emergence to protect natural enemies.
Research
A biological control program was initiated at the Western Triangle Ag Research Center. A parasitoid Macroglenes penetrans was introduced from Alberta and established in Montana in 2014. Efforts are underway to introduce two additional parasitoids (Euxestonotus error and Platygaster tuberosula) from Saskatchewan.
